The role of the endocannabinoid system is for maintaining balance, health and wellbeing in both humans and other species. Without the engagement of the endocannabinoid system, our bodies probably would not be able to recover from an inflamed wound or even the common cold. If you’re curious to find out how cannabis affects the body, keep reading this article about the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoid might seem like a sciency word that has no importance whatsoever to a cannabis user – but it is the system in the body that interacts with cannabis when you ingest it. The endocannabinoid system is the internal system of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors that live in the human body.
In fact, the cannabinoids inside your body are extremely similar to the cannabinoids that come from cannabis. The endocannabinoid system is responsible for maintaining balance, and plays a crucial role in healing when a body has become sick.
Humans aren’t the only creatures with an endocannabinoid system, either. It exists in all mammalian brains and bodies, evolving around 600 million years ago. Even our pets have an endocannabinoid system. It arguably connects us with the greater “balance” of the mammalian world, and even the plant world!
In short, the endocannabinoid system is essential to the existence of all mammals and their ability to stay healthy and happy in this world. Without it, the other systems in our body would likely come out of balance with each other.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
Believe it or not, it was the discovery of cannabinoids within weed itself that led to the discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system (otherwise known as the endocannabinoid system).
It was discovered by Raphael Mechoulam, an Israeli chemist who had a particular interest in cannabis. It was his attempts at isolating cannabinoids that finally led to the discovery of the body’s most important physiological system for maintaining health. After successfully isolating THC, Mechoulam discovered the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide. This discovery snowballed into the epic realization that we contained this system within our own bodies!

It is a system that works in the central nervous system as well as neurologically. Endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid receptors exist all around the body and brain for this reason, throughout organs, tissues, immune cells and glands. At the end of the day, the endocannabinoid system has many roles and functions within the body. However, the aim is ultimately the same every time – homeostasis – meaning bringing the body and brain back into balance and working order.
What are the functions of endocannabinoids?
There are many processes within the body that are regulated by the endocannabinoid system. As well as being present in the immune system, they are also present in the neurological system. This means their reach goes so far as your sense of hunger, your sense of pain, how quickly wounds and inflammation heal, and even so far as your sexual desire. Essentially, endocannabinoids are working in the body to regulate any process that has come out of balance.
The main way that endocannabinoids undertake this enormous task is through the process of cell-signalling or cell communication. They live in many of the cross sections between systems in the body, and they allow the communication between different parts of the body.
In this way, cannabinoids can target many different cell types with a single “action” or “signal”. For example, the endocannabinoid system is kicked into gear at the instance of an injury. At the site of that injury, cannabinoids are communicating to reduce inflammatory cells, as well as to prevent the nerve cell from firing excessively.
The most well-known endocannabinoid is called anandamide, otherwise known as the bliss molecule. It acts as a neurotransmitter, essentially being a messenger.
Anandamide delivers messages to many parts of the body, regulating things like appetite, pain sensation, memory and even fertility. The chemical structure of anandamide is almost identical to THC, and it has many of the same effects. This is probably why THC works so well for humans: It mimics the effects of this natural endogenous cannabinoid.
Cannabinoid receptors
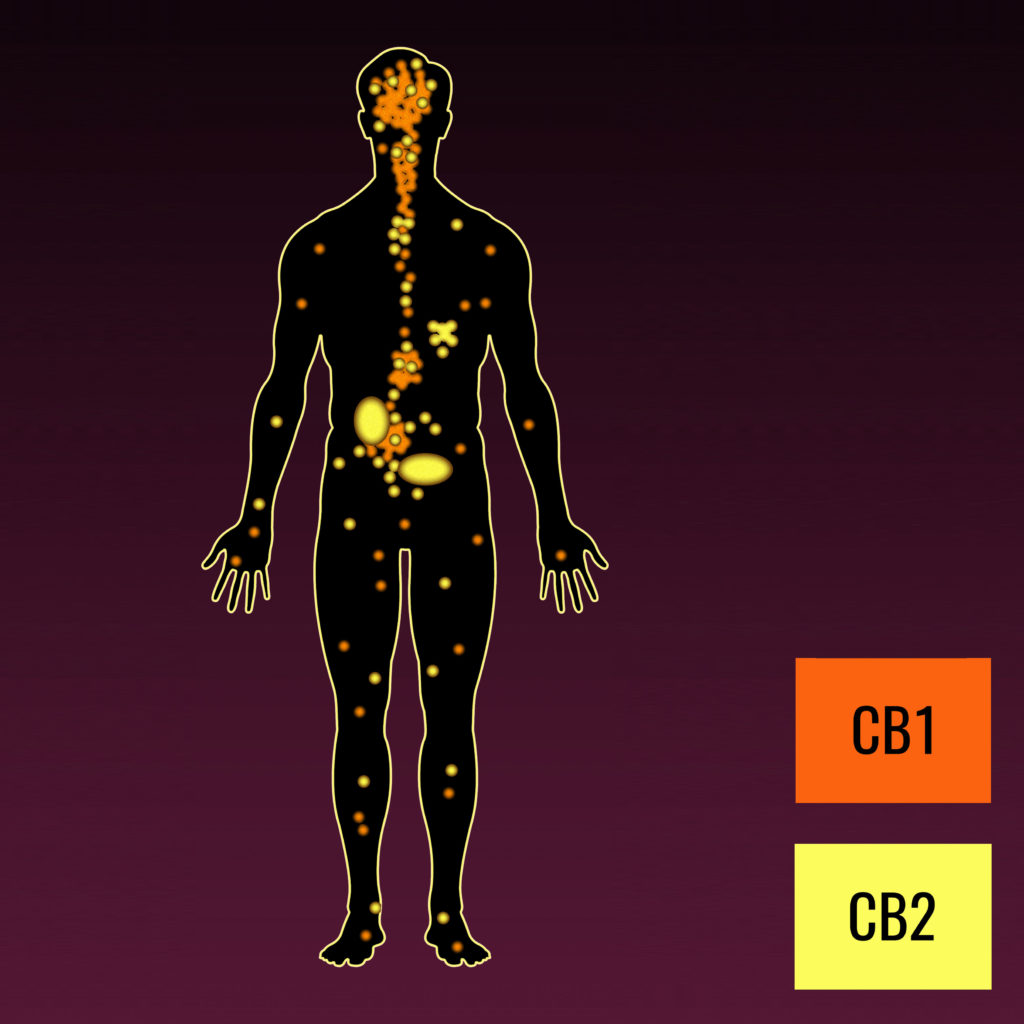
Scientists have only discovered two cannabinoid receptors since the discovery of the endocannabinoid system. CB1 and CB2 are the names of the two discovered receptors, and are found in the nervous system (connective tissues and glands) and the immune system respectively.
The CB1 receptor mediates psychoactivity, while the CB2 receptor is responsible for immune function and response. When these receptors are excited, all of the magical and wonderful biological processes of the endocannabinoid system begin to take effect.
They are spread out through the entire body and there are thought to be many more that we have not discovered yet. Ultimately, these are the two cannabinoid receptors that we know about because of their interaction with cannabinoids coming into the body from cannabis use.
Having said that, they do not act only when excited by external cannabinoids. Even without using cannabis, the CB1 and CB2 receptors can be excited into action.
Promoting overall health and wellbeing
The profound communication that takes place in the body through the endocannabinoid system is seen as something like a link between the body and the mind.
Our limited understanding into the endocannabinoid system is beginning to show us a link between emotional/mental wellbeing and physical wellbeing, as the endocannabinoid system also has a hormonal and emotional effect. The homeostasis that is restored in the body also felt in the mind, and on observation, of the world at large.
Humans are not the only creature graced with an endocannabinoid system, as it is something we also share with all other vertebrate species, nematodes and sea squirts.
This might explain why some other animals are also fond of the cannabis plant (and we consider them pests to it!) – it also works to encourage their own endocannabinoid systems. The presence of an endocannabinoid system in other species is what suggests that the greater ecosystem is affected by its activity.
The endocannabinoid system has the ability to work with many different aspects of both humans and other mammals. This is what makes it so important to our wellbeing.
It is not localized, in the sense that it does not necessarily target one specific area all the time. Sometimes the endocannabinoid system is taking effect hormonally, and at other times it is taking effect in the organs. It does not behave a certain way, but rather it behaves in the way that will restore homeostasis to the individual.
Cannabis joins the equation
The addition of cannabis to the human endocannabinoid system begins one of the most magical alchemical reactions in human history. Actually, it seems that somehow this external substance and our internal system were made to work with one another. They are basically made up of the exact same stuff, and so what happens when the individual uses cannabis is that they are engaging the part of their body that plays a role in balance and wellbeing.
The use of cannabis (at least medically speaking) is less concerned with handling the symptoms of disease than it is with activating the part of the body that can do the healing. The symptoms that require medical attention are secondary to activating the balancing system itself.
Weed does exactly that, especially in those for whom the endocannabinoid system is dysfunctional. By stimulating the CB1 and CB2 receptors from an external source, weed activates the healing processes that are governed by the endocannabinoid system.
There are many different cannabinoids in the hemp and cannabis plants, and they target different receptors for different reasons. Cannabis communicates with the human’s endocannabinoid system for the fundamental purpose of harmonizing, which is why it has been coined a miracle plant.
Nature is a healer in and of itself, and the discovery of the endocannabinoid system is basically evidence of this. The more our knowledge grows of both the endocannabinoid system and cannabis, the more we become of how cannabis plays a role medicinally.